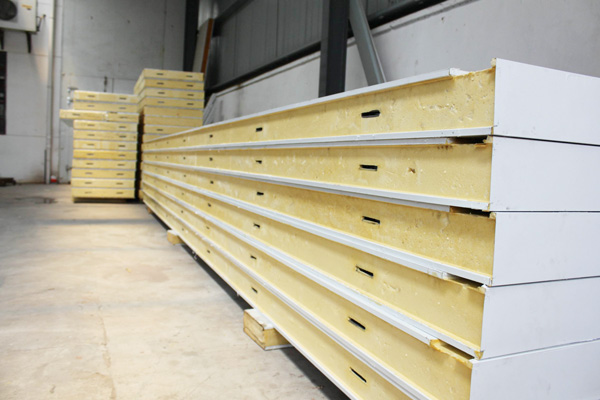
Cold storage panels
Description of Cold Storage Panels
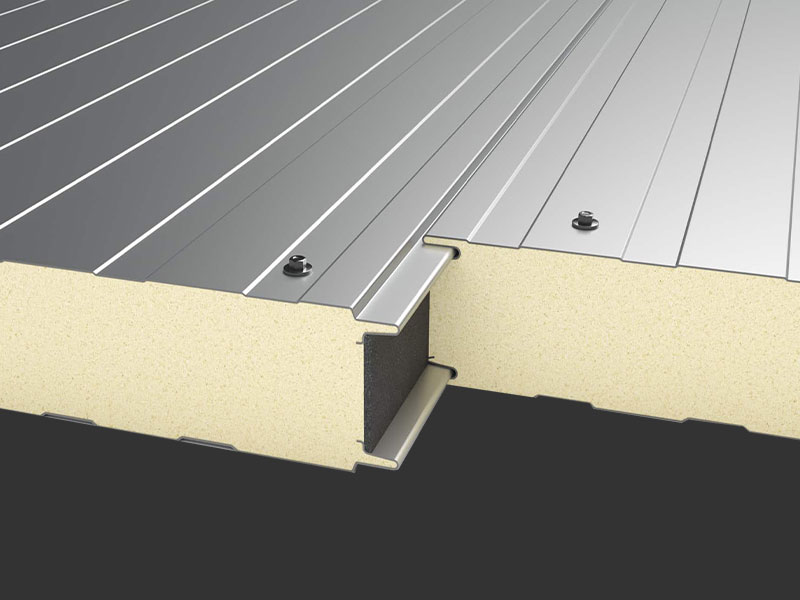
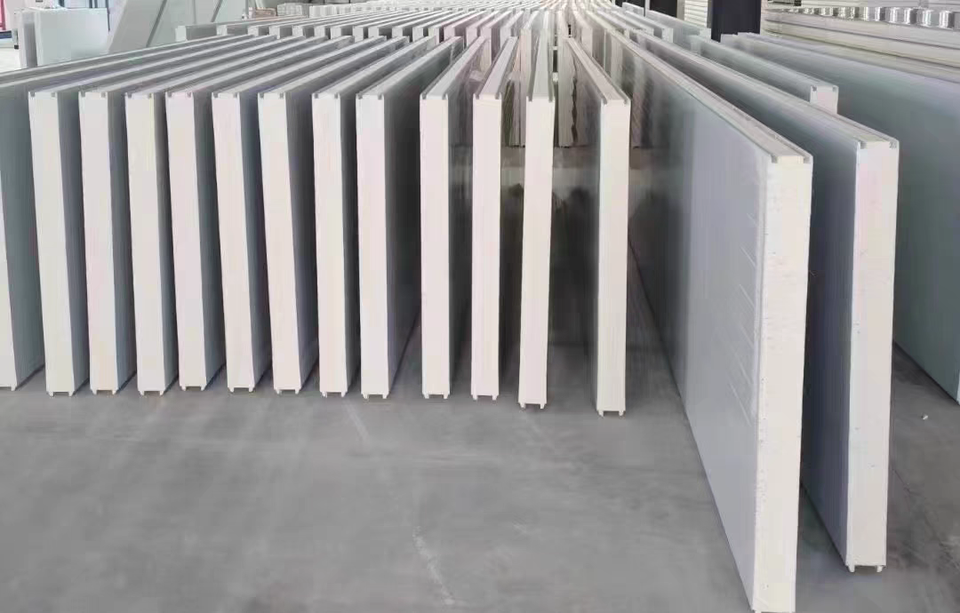
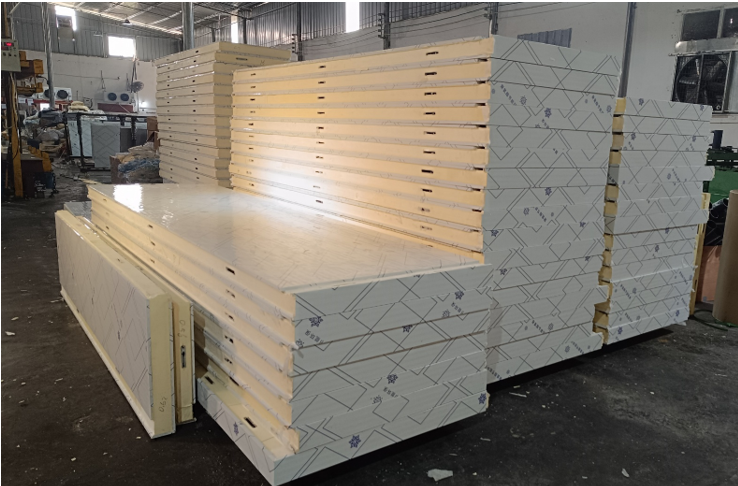
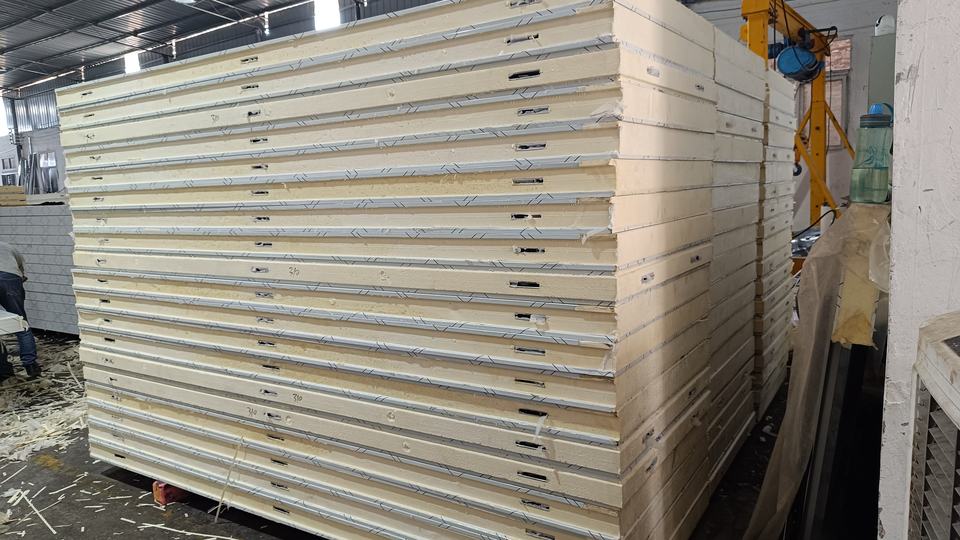
Cold storage panels are sandwich-structured composite panels featuring double-sided colour-coated steel or stainless steel facings with a high-density polyurethane core. They achieve tight jointing through built-in eccentric hook fasteners, offering exceptional thermal insulation properties. These panels are specifically designed for constructing cold storage facilities across various temperature grades.
Core characteristics of cold storage panels

High-efficiency insulated door panels
The door panels feature a high-density polyurethane (PU) high-pressure foam moulded in one piece, offering low thermal conductivity and exceptional insulation performance. Available thicknesses (e.g., 100mm/150mm) effortlessly accommodate diverse temperature control requirements, from fresh-keeping chambers to ultra-low temperature freezers (-45°C).

l Professional-Grade Sealing System
Perimeter door seals employ low-temperature resistant, anti-ageing EPDM rubber gaskets. Combined with specially engineered door frames, these create a perfect airtight cavity upon closure, effectively preventing cold air leakage and heat ingress.

l High-Performance Track System:
Features high-strength aluminium alloy tracks with robust load-bearing capacity. Surfaces undergo anodised treatment for corrosion resistance and wear durability. Paired with silent nylon rollers, these tracks enable smooth, quiet manual or automatic operation even for heavy doors.

l Robust and Durable Construction
Door panel surfaces can be finished in colour-coated steel, stainless steel, or similar materials, offering not only aesthetic appeal but also impact resistance, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning. The scientifically engineered overall structure ensures minimal deformation under prolonged, high-intensity use.

· PrFood processing workshops
· Cold stores and freezer rooms
· Cold chain logistics centres and distribution warehouses
· Pharmaceutical factories and cleanrooms
· Biological laboratories and sample repositories
· Flower preservation chambers
· Low-temperature storage for
|
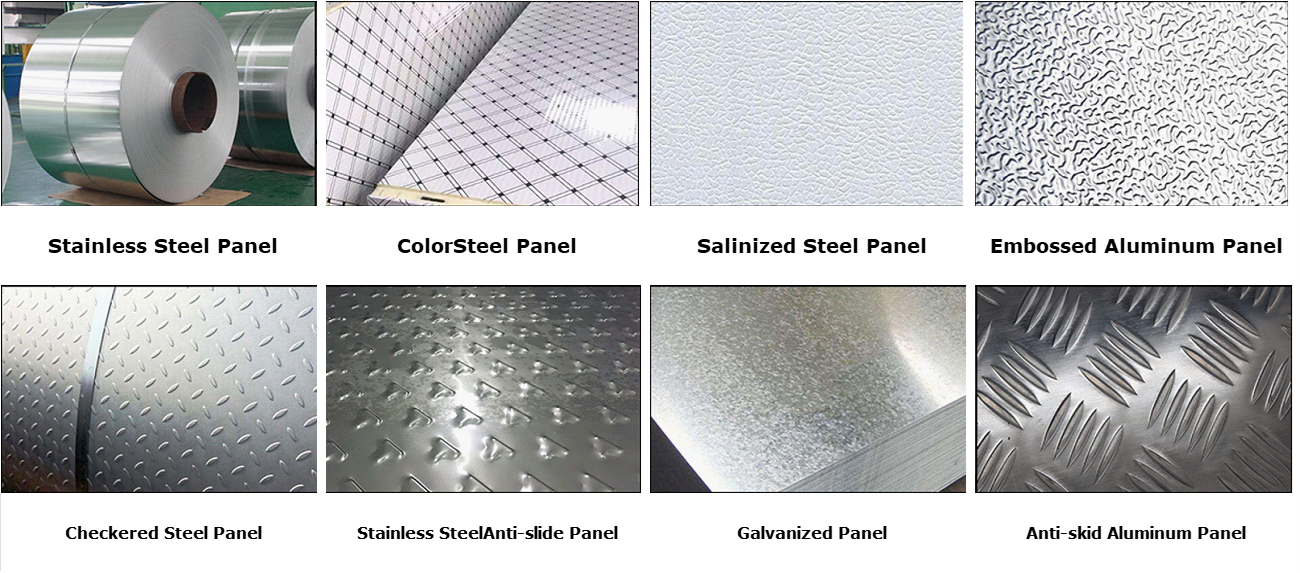
Surface Material |
Surface Material Thickness |
| Double-sided color steel | 0.326/0.426/0.476/0.5-1.0 |
| Double-sided stainless steel | 0.4/0.45/0.5/0.55/0.6-0.8 |
| Double-sided salinized steel | 0.4-1.0 |
| Double-sided embossed aluminum | 0.5-1.2 |
| Color steel+stainless steel | 0.5-1.0 |
| Color steel+salinized steel | Optional |
| Color steel+galvanized panel | Optional |
| Color steel+checkered steel panel | Optional |
| Color steel+anti-skid aluminum | Optional |
| Color steel+stainless steel anti-slide panel | Optional |
Surface Material Selection

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Cold Room Panels
Here is a list of common questions to help you understand the specifications, benefits, and applications of cold room insulated panels.
1. What is a cold room panel?
A cold room panel, also known as a sandwich panel or insulated panel, is a structural component used to build walk-in coolers, freezers, and other temperature-controlled environments. It typically consists of an insulating core material sandwiched between two metal sheets.
2. What are the core materials used in cold room panels?
The most common core materials are Polyurethane (PUR), Polyisocyanurate (PIR), and Expanded Polystyrene (EPS). Both PUR and PIR offer excellent thermal insulation, while PIR has superior fire resistance.
3. What is the difference between PUR and PIR panels?
While both are polyurethane-based foams, PIR (Polyisocyanurate) panels are chemically structured to offer significantly better fire retardant properties and higher thermal stability compared to standard PUR (Polyurethane) panels.
4. How do I choose the correct panel thickness?
The required panel thickness depends on the desired operating temperature. For a walk-in cooler (0°C to 10°C), 75mm or 100mm is common. For a walk-in freezer (-18°C to -25°C), thicknesses of 120mm, 150mm, or even 200mm for blast freezers are recommended to ensure energy efficiency.
5. What is the R-value of a cold room panel?
The R-value measures a panel's resistance to heat flow. A higher R-value indicates better insulation performance. PIR and PUR panels have a very high R-value per inch, making them highly effective for cold storage applications.
6. What is a cam-lock system?
A cam-lock system is a mechanism embedded within the panels consisting of a hook and pin. When tightened with a hex key, it pulls the panels together, creating a strong, airtight seal. This system simplifies installation and allows for easy disassembly.
7. Are there other joint systems besides cam-locks?
Yes, another common system is the tongue and groove joint. This design allows panels to interlock, providing a continuous insulation barrier and preventing thermal bridging. It's often used in conjunction with sealant for a perfect seal.
8. What types of metal facings are available for the panels?
The standard facings are pre-painted galvanized steel (PPGI). For environments requiring high hygiene standards, such as food processing or pharmaceutical storage, stainless steel or PVC-coated steel facings are also available.
9. What is the fire rating of cold room panels?
The fire rating depends on the core material. PIR panels typically achieve a higher fire resistance classification (e.g., B-s1, d0 under Euroclass standards) compared to PUR or EPS, making them the preferred choice for projects with strict fire safety regulations.
10. How do insulated panels contribute to energy savings?
Their high-performance insulating core minimizes heat transfer between the ambient environment and the cold room. This reduces the workload on the refrigeration system, leading to lower energy consumption and significant cost savings.
11. Can cold room panels be used for ceilings and floors?
Absolutely. The same insulated panel system is used for walls and ceilings. For floors, special reinforced floor panels capable of withstanding forklift traffic and heavy loads are available, often with a durable non-slip surface.
12. What is the density of the insulation core and why does it matter?
The density of the foam core (typically 38-42 kg/m³ for PUR/PIR) is crucial for both its structural strength and its thermal conductivity. A proper density ensures long-term stability and optimal insulation.
13. Are the panels waterproof and airtight?
Yes, when installed correctly, the panel joints (whether cam-lock or tongue and groove) and the impermeable steel surfaces create a complete vapor barrier. This prevents moisture ingress, which can degrade insulation and cause ice buildup.
14. Can I get custom-sized panels for my project?
Yes, manufacturers can produce custom-sized panels to fit the specific dimensions of your project, minimizing waste and ensuring a perfect fit for a highly efficient cold storage solution.
15. How are the panels maintained and cleaned?
The smooth metal surfaces are easy to clean with mild, food-safe detergents and water. Regular cleaning is important to maintain hygiene, especially in food processing and pharmaceutical applications.
16. What is the typical lifespan of a cold room panel?
High-quality sandwich panels made with a durable steel finish and a high-density PIR/PUR core can last for over 20-30 years if properly installed and maintained.
17. Can damaged panels be repaired or replaced?
Minor surface damage can often be repaired. For significant damage to the core or metal skin, the modular nature of the cam-lock system makes it relatively easy to replace an individual panel without dismantling the entire structure.
18. What are the primary applications of these panels?
Key applications include cold storage warehouses, distribution centers, supermarket cold rooms, food processing facilities, pharmaceutical storage, clean rooms, and agricultural storage.
19. What does "thermal conductivity" (λ-value) mean?
Thermal conductivity (λ-value) measures how easily heat passes through a material. A lower λ-value means better insulation. PIR and PUR foams have very low thermal conductivity, which is why they are excellent insulators.
20. What factors influence the cost of cold room panels?
The main cost factors include the type of core material (PIR is typically more expensive than PUR), the panel thickness, the type of steel facing (stainless steel is the most expensive), the fire rating, and any custom specifications.










